Upgrading MIT HandyBoard to 64KB
1. What
is required
2. Description
3. Preparation
4. Upgrading
5. Testing
6. Conclusion
7. Downloading
8. New memory map
9. Pictures
Having only 32KB of RAM for
the Java applications can be many times annoying limitation,
especially if you want to use floating point version of the VM
and the size of the Java application is getting close to the
16KB limit (see the HB's
current memory map).
Fortunately, there is a way out. If you have spare 62256,
couple of logic gates ICs and are skilled in soldering you can
have HandyBoard running with 64KB of RAM in less than 60
minutes.
This
upgrade should be carried out only by a person
familiar with:
- basics
of digital circuitry
- handling
devices sensitive to static electricity
- fine
soldering
Any
inappropriate manipulation may cause damage to your
HandyBoard.
|
What is required
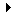 |
1x
62256-100LP. It is recommended to use the same brand
name and speed of the memory chip as the one used on
your HandyBoard. |
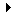 |
1x 74HC132 |
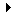 |
1x 74HC20 |
 |
PD5/SS pin
on 68HC11free for activating additional 32K RAM |
Description
The HandyBoard has been originally designed in
such way that 32KB RAM is mapped to upper 32K memory area
(0x8000 - 0xFFFF). Lower 32K memory area is used by the
68HC11's internal RAM (0x0000 - 0xFF), system registers
(0x1000 - 0x103F) and eight memory mapped chip selects
(U6/74HC138). See the documentation provided with HandyBoard
if you'd like to learn more about it's hardware.
In order to use additional
32KB of RAM (at 0x0000 - 0x7FFF) it is necessary to disable
memory mapped chip selects (U6) while accessing the RAM below
0x8000. This is accomplished by connecting the pin G1 of U6
(via glue logic) to the PD5/SS pin on 68HC11.
After the reset, 68HC11 sets
all pins on PORTD as input. External 10K resistor on PD5/SS
pin sets the default logic levels in such way that memory
configuration is fully compatible with 32KB version of the
HandyBoard. Under the software control the PD5/SS pin can be
programmed as output. Writing logic 1 to PD5/SS pin will
enable chip selects on U6 and disable additional 32KB RAM at
0x0000-0x7FFF. Setting this pin to logic 0 will disable chip
selects on U6 and enable additional 32KB RAM.
The Java VM itself doesn't
control PD5/SS pin, however, the HandyBoard's native code has
been modified to make all 64KB of RAM active all the time
except for the moments when peripherals connected to U6 are
being accessed.
Preparation for memory
upgrade
| 1. |
Download
the schematic
diagram (11 KB PDF file) |
| 2. |
Get the
following components:
1x 62256-100LP
1x 74HC132
1x 74HC20
1x 10K resistor
fine enameled copper wire |
| 3. |
If
components on your HB are in sockets then remove U2,
U7 and U9.
If components are soldered then the ICs listed above
would need to be soldered directly on the HandyBoard. |
| 4. |
Lift G1
pin on U6 (pin #6) so it doesn't connect anymore to E
clock. If U6 is soldered, cut this pin with fine side
cutters at the bottom of the board and then lift it up
a little bit. |
Making the upgrade
| 1. |
Stack the
62256 chips on top of each other (UX3 on U2). Solder
all pins together except for pin #20 on UX3. This pin
should be lifted or cut short so it doesn't touch pin
#20 on U2. |
| 2. |
Stack the
74HC132 on top of each other (UX1 on U7). Solder pins
#7, #12 and #14 together. All other pins on UX1 should
be lifted or cut short so they don't touch pins on U7. |
| 3. |
Stack the
UX2 (74HC20) on top of U9 (74HC04). Only power ground
pins (#7) should be soldered together. All other pins
on UX2 should be lifted or cut short to avoid contact
with pins on U9.
Note: As only pin #7 are soldered use a drop of
superglue between the UX2 and U9 so they hold together
firmly. |
| 4. |
Place
soldered ICs back into sockets. |
| 5. |
Use
enameled copper wire to interconnect all components as
indicated on schematic diagram. |
Testing the HandyBoard
| 1. |
If
everything has been done properly you should be able
to load any current application (Java or Interactive
C), provided it doesn't use PD5/SS pin on the 68HC11. |
| 2. |
To get
advantage of the extra 32KB of RAM download the
specially modified Java application DemoHB64 (or
DemoHB64Exp) that utilizes the new memory
configuration. |
Conclusion
One limitation on use of
the RAM below 0x8000 is that the code being executed from here
can't access peripherals activated by U6 directly. All
subroutines accessing the U6 (and thus switching off RAM below
0x8000) must be located above 0x8000.
This limitation, however, doesn't apply that much if using
Java on the HandyBoard as lower memory space is used just for
storing Java application code. The Java application code is
interpreted by the VM and native code that are located above
0x8000.
To make maximum use of the
new 32KB RAM, the system registers are re-mapped from 0x1000
to 0x8000. This gives Java application continuous space of
almost 32KB. Being able to have 64KB of RAM allows to increase
heap size to 16KB (see the HB's new memory
map).
It would be probably possible
to use the 64KB HB with the Interactive C, but somebody would
need to update internal routines (pcode,...) that access the
chip selects on U6 so they are compatible with the new memory
structure.
Downloading demo applications
After downloading and
installing the appropriate file open the readme-hb64.html for
additional information about the software.
DemoHB64 application
for HB without expansion board
DemoHB64.exe
(461KB) self-extracting archive for Windows
DemoHB64.zip
(432KB) zip archive for other platforms
|
| DemoHB64Exp
application for
HB with expansion board attached
DemoHB64Exp.exe
(460KB) self-extracting archive for Windows
DemoHB64Exp.zip
(430KB) zip archive for other platforms
|
Installation instructions
If you have downloaded
self-extracting archive run it by double-clicking on it from
the explorer. You will be prompted for destination folder.
Select the folder where you have previously installed Java VM
for 68HC11. Then click on the Unzip button. When installation
finishes select the Close button.
If you have downloaded zip
archive, unzip it into the root of Java VM for 68HC11
installation with create sub-directories and overwrite
files options enabled.
HandyBoard's new
memory map
| $FFFF
$C000
|
Garbage
collected heap memory for runtime objects created by
the Java application |
16KB |
| $BFFF
$BFD6
|
Location
of interrupt vectors when using 68HC11 in special
test mode |
42
bytes |
| $BFD5
$9700
|
Memory
space for
Java VM code (with FP) & data |
10.2KB |
| $96FF
$8040
|
Startup/native
code & data space |
5.7KB |
| $803F
$8000
|
Re-mapped
68HC11 control registers |
64
bytes |
| $7FFF
$200
|
Memory
space available to the Java application |
~32KB |
| $00FF
$0000
|
68HC11
internal RAM loaded
with LCD driver during init. sequence |
256
bytes |
Pictures of the modified HandyBoard
| 
